Life on Earth began in water and evolved from it. You have personal experience with this dependence each time you seek water fluids to quench your thirst and replenish your body’s water content. The cells inside your body are surrounded by a fluid that is mostly water and your cells themselves range from 70% to 80% in water content. Water is the biological medium here on Earth and the supporter of all life forms.
Water circulates through our body without rest and causes the macromolecules (proteins, enzymes, and genes) and cells in the body to function properly. When information is passed from tissue to tissue, it is water that delivers this information. Water performs not one but many particular tasks, all life-supporting or life-saving. In a living body, if the circulation of water slows down too much, life ceases. Equally important to both lower and higher organisms, water is the vital generator of life and its supporting force.

Every day you make an assumption about the safety of the water you drink. Whether that trust is well-placed, is the real question.
Our natural water resources are under a great deal of stress, as we battle with an ever changing climate, pollution and the needs of a rapidly growing population. Demand for quality drinking water has never been greater!
Our government has a duty to provide us with water that is safe to drink, however the water quality at the point of consumption may not always be complimentary for our short or long-term health. Contaminants including heavy metals, chemicals such as chlorine, pesticides, bacteria, organic & in-organic compounds all can be present in our drinking water.
Given the importance of water to our wellbeing & every bodily function, we owe it to ourselves to ensure that the water we drink is as pure & fresh as possible!
We don’t all have a natural spring water source in our back yard & purchasing pre-bottled water can be both inconvenient and is prohibitively expensive, both financially and environmentally.


Contact us for more information.…

Centuries ago, if you wanted to filter your water at home, you’d likely have to boil the water then pour it through sieve-like cloth bags to trap sediments that caused foul taste and smell. Water filtration was no more complex than that, at least not until thousands of years later. Nonetheless, continuous efforts to obtain “clean” drinking water led to many breakthroughs in water filtration throughout the ages.
These days, we have access to a vast array of modern home water filters equipped with state-of-the-art features and technologies to help produce the cleanest, purest, and highest-quality water possible. As a result, clean drinking water has become so widely available today that many people take it for granted.
Modern water filters can treat large quantities of water, usually behind the scenes, with little to no human intervention. However, while you can find these devices in many American households, very few of us know their origins and evolution. Sure, these systems may seem like a new development, especially if you live in an area with limited access to clean water, but they have a history that stretches back thousands of years.
In this post, we’ll be tracing water filters back to their origins, how they’ve evolved through the ages, and what’s their state in this modern era.
The earliest attempts to discover or produce pure water go as far back as 2000 BC. During this period, Ancient Greek and Sanskrit methods ranged from boiling or placing hot metal instruments in water before drinking it to filtering that water through crude sand or charcoal filters. People developed these methods to provide better-tasting drinking water because, during that time, they determined water purity by taste. They did not (or couldn’t) yet connect impure water with diseases, nor did they have the technology necessary to recognize tasteless yet harmful microbes in drinking water. They knew to try to reduce cloudiness, objectionable taste, and appearance in water but didn’t know much or any at all about chemical contamination or microbes.
As early as 1500 BC, the Egyptians discovered the principle of coagulation, which involved using alum to clarify water. The alum caused suspended particles to settle in the water, after which people would skim the “clean” water from the top of the container.
Centuries later, around 500 BC, Hippocrates, the famed father of medicine, designed a crude water filter to “purify” the water he used for his patients. This filter was later known as the “Hippocratic sleeve.” It was essentially a cloth bag that they poured the water through after boiling it. The cloth would trap any sediments in the water that were causing bad taste or smell.
For over 1,000 years, there was very little to no interest shown in water purification, leading to a lack of improvement. However, in the 1600s, Sir Robert Bacon began experimenting with sand filtration as he attempted to remove salt from seawater. While his desalination experiment was unsuccessful, he laid the groundwork for other scientists to get involved in the field. In the 1670s, the microscope was invented, and with its invention, humans would be able to detect microscopic organisms and other particles in water. During this time, scientists created the first multi-stage filter. Both these inventions proved beneficial to the water treatment process.
In the mid-1700s, Joseph Amy obtained the first patent for a water filter. His design incorporated charcoal, wool, and sponge layers to eliminate unwanted organisms and particles. These filters were made available for sale in 1750. By the late 17th century, the development of the microscope had given scientists new insights into the innumerable microorganisms present in water. Soon after, water filtration became the preferred water purification method for many communities as they started using domestic water filters. While these filters weren’t perfect, they were indeed a considerable improvement on anything introduced before.
In 1804, Robert Thom designed the first municipal water treatment plant, later built in Scotland. The treatment was based on slow sand filtration, and horse-drawn carts distributed the treated water to communities and cities. Some three years later, the first water pipes were installed. The suggestion was that every person should have access to safe drinking water, but it would take somewhat longer before this was brought to practice in most countries.
In 1854, a breakthrough came via an unfortunate event. Researchers discovered that an epidemic of cholera infection spread through water and that the outbreak had been less intense in areas that had sand filters. British scientist John Snow found that it was sewage water contaminating the water pump. After several experiments, he also found that chlorine could be used to purify the contaminated water, which would then establish the practice of chlorination for water disinfection.
During that time, the water had smelled and tasted fine, so this was when they concluded that those factors weren’t enough to guarantee the safety of drinking water. As a result, cities began installing municipal water filters, and government water regulation became the norm.
By the late 18th century into the 1900s, significant advances were made in the water filtration arena. While slow sand filtration became popular in water filter systems in many European and American cities, it used up a lot of land space and could not keep up with the rapid population growth. As a result, rapid sand filtration was introduced to improve slow sand filtration’s speed and efficiency.
Thom’s slow sand filters included two main features: the reverse flow wash and the false bottom. The issue was that they used mechanical agitators for loosening debris and water jets or backwashes for cleaning filter media. On the other hand, rapid sand filtration involved pretreatments, such as coagulation and settling to reduce sediment load on the filter, and charcoal filtration for improving the water’s taste and odor. Besides, the rapid sand filters used a Jetstream to clean the filter and improve its capacity.
At the same time, more and more cities were building water treatment facilities and using several filtration methods, along with water chlorination and ozone, to help purify water. As these methods became more widespread, the outbreaks of waterborne illnesses like cholera and typhoid declined. However, it wasn’t long before chlorination started to reveal its dark side. Research linked chlorine ingestion to various respiratory diseases and other health effects, forcing experts to search for alternatives.
Realizing the importance of providing clean drinking water for its residence, America passed the Clean Water Act of 1972 and the Safe Drinking Water Act of 1974, which were developed on the premise that everyone has a right to safe water. This was also when the major public health concerns about drinking water shifted from disease-causing microbes to manufactured pollutants like pesticides, industrial sludge, chemicals, etc. By the 1980s, researchers developed the first membranes for reverse osmosis systems after previously developing effective treatment methods, such as aeration, flocculation, and granular-activated carbon absorption for removal of organic contaminants. As advances in technology and competition grew, it paved the way for modern, sophisticated water filtration methods, many of which are still used today.

Before deciding on a filter, consider some important factors that can help you make the best decision, including the type of filter, material, flow rate, and installation requirements. By understanding these features, it’s easier to decide which option would be the best faucet water filter for your home.
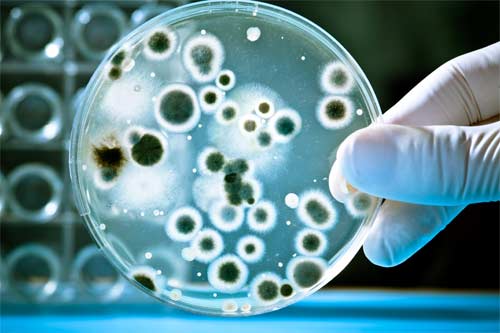
There is a wide range of contaminants that can be present in tap water, including pesticides, microorganisms, organic compounds, chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and harmful heavy metals such as lead, mercury, and arsenic. Water contaminants vary by community, and knowledge is power. Start by researching what’s affecting your own water supply through the National Drinking Water Database created by the Environmental Working Group.
Always check to make sure the filtration system can take care of the contaminants you’re most concerned about. Regardless of which microscopic contaminants they’re best at keeping out of drinking water, faucet-mounted filters considerably improve the taste of H2O.
Faucet water filters are typically made with either plastic or stainless steel. Some manufacturers may offer a range of different finishes, but these are usually stainless steel filters that have metal plating over the original material just to give it a different look. So the decision comes down to plastic or stainless steel.
Flow rate refers to the amount of water that flows through the filter within a set time period and it’s typically measured in gallons per minute (GPM). Whole-home water filters must be capable of filtering many gallons of water per minute since most showers and dishwashers can use up to 5 GPM.
However, faucet water filters don’t have the same water pressure demands. Most of these smaller filters have a set flow rate of 0.5 GPM with very few exceptions. This is about enough to fill up seven or eight standard glasses of water in 1 minute.
The filter life is typically indicated in the product information or on the manufacturer’s website. After this time period, the filter becomes less effective until it does very little except get in the way of regular faucet use. However, the total life of one filter can differ significantly from other, even identical products. This is due to usage.
Filter life is tied directly to usage. When the faucet is left running, it wastes water and also reduces the filter life, forcing the user to replace the filter cartridge at a higher frequency. By using the filter only for drinking water or cooking water, you can extend the life of the filter, saving time and money.
When the filter starts to lose its effectiveness, the entire faucet-mounted filter does not need to be replaced. Simply remove the filter cartridge and replace it with a new cartridge. Most manufacturers also produce cartridge replacements, so it’s easy to find a compatible option.
These cartridges typically have a lifespan measured in gallons of water that can range from 100 to 1,000 gallons, depending on the product. After a certain amount of water has been filtered through the cartridge, it begins to lose effectiveness. Some filters also come with cartridge replacement recommendations from 1 month to 3 months so that it’s not necessary to try and measure the amount of water flowing through the filter.
Most faucet water filters have a plastic or a stainless steel design, but this doesn’t prevent manufacturers from adding additional color options and metal finishes, giving options to match the aesthetics of a home.
After …
/purnewadvancedfilter-566774ae5f9b583dc3c492ff.jpg)
There are two reasons to get a water filtration system, explains Rick Andrew of NSF International, a health and safety standards testing company that certifies water filtration systems. Because drinking water in the U.S. is generally very safe, it’s more likely that you’ll want a water filter to improve taste or remove hard minerals and protect your pipes; hard water (i.e., water with high mineral content) can damage pipes and water fixtures with buildup.
However, there are still times when you may want a system that can filter out more dangerous contaminants like lead or man-made chemicals that are increasingly present in our water. If you are on well water, have old pipes, or live in an area with unsafe drinking water, you may need a water filter to remove contaminants like lead or to remove actual particles like sand.
If you are on city water, you can look at the annual water reports to see what kinds of contaminants are in that water. Even if your municipal water is safe, you may have old pipes that could be leaching contaminants into your water. Adding a water filter can help remove those impurities. Filters certified to remove chlorine, for example,bestmixer.mx can also encourage hydration by making water more enjoyable to drink.
Because effective filtration is so important (and because it’s so hard to actually be able to tell if it’s working), certification is one of the only ways you can actually be sure your water filter is removing the contaminants its packaging claims it is. The NSF, where Andrew works, is one certifying body. Other certifications to look for are the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) and the Water Quality Association (WQA). There is no one-size-fits-all certification, so it’s important to know what you want removed from your water. For example, the NSF offers certification for removing a certain amount of chlorine and a separate one for removing lead. The more certifications a filter has, the more contaminants it can remove.
Andrew cautions that you just need to make sure it’s actually certified. Marketing jargon to look out for is things like “filters to NSF standards,” which does not mean it has been independently tested. An earlier version of our list included several water filters that were removed based on similar language that made it unclear whether they were independently tested.
You will also want to consider your household’s water consumption when purchasing a filter. A smaller pitcher for a dorm or apartment, for example, may be fine. But for larger households (or if you want to filter water for cooking as well as drinking), faucet or under-sink filters may make more sense. Refilling a pitcher doesn’t take a huge amount of time, but if you need to do it several times a day, it can be easy to give up on it and simply go back to drinking unfiltered water from the tap.
Filter cost is another thing to consider. A water filtration system is only as good as its filters, so be sure to factor them in, including price, availability, and how often they need to be replaced when deciding on your filtration system.
Water filtration systems can either cost thousands of dollars or, if you’re getting a small pitcher, around $20. The good news is that both systems can effectively remove contaminants from the water. You can get an affordable water filter for personal use without spending much—but make sure to look for certifications. Also, consider the cost of the water filter and how often it will have to be replaced when deciding what you want to spend.

When we think of water filters, a pitcher is the first thing that comes to mind, but water filters can be used at almost every point of water’s journey through your home.
Whole-home systems filter all the water coming into your home. The most common kind, says Andrew, is a water softener that will help remove minerals and “soften” your water. Since hard water is bad for pipes and water fixtures, a whole-house filtration system makes the most sense. Because this type of system filters water for the whole house, it’s often expensive and time-intensive to set up.
If you are filtering for contaminants or taste in your drinking water, a point-of-use filter is also an option. These can be filters that attach to the sink or under the sink where you get drinking water. Andrew emphasizes that whole-house filtration, unless you are on a well, is generally only for softening water, and that these point-of-use systems are sufficient if you’re filtering out contaminants. Under-sink filters are often easier to install than whole-home systems, but are more expensive than faucet attachments or pitchers.
Like under-sink filters, faucet attachments offer instant access to filtered water at a place where you would be getting drinking water, such as the kitchen sink. These filters can typically be attached to most standard sinks, though they won’t work with more unique sink setups, like a pull-down faucet with a spray nozzle. A faucet attachment will typically allow you to filter only the water you want to drink, and let unfiltered water come through for things like washing dishes. If your water is safe and you are only filtering it to improve taste, this should be sufficient. This type of system also puts less pressure on the filter by only filtering the water you need.
Pitchers don’t offer the convenience of a sink filter because they need to be refilled. But, Andrew points out, some people prefer pitchers because they allow you to chill filtered water, which can make it more enjoyable to drink. It’s also the easiest to set up. Furthermore, if you are only filtering water for taste, you may find a faucet filter to be bulky and unnecessary while you do things like wash dishes or your hands at the sink. But, again, this comes down to preference, and both faucet attachments and pitchers are capable of filtering out contaminants.
Countertop water filtration systems work similarly to faucet filters by diverting water from the sink into a filtration system with its own tap. Other countertop filtration systems need to be filled, acting like water coolers; these can be bulkier than pitchers, but require less frequent refilling. They do offer the advantage of allowing you to place filtered water anywhere in your home, away from a water source.
Water bottles can also filter water and thus be certified by the NSF and ANSI. They can filter water as you fill the water bottle or as you drink it. Water bottles can be a great option if you want to drink filtered water on the go, and they’re a great alternative to buying water bottles. But many home water filtration brands and filters are designed to remove contaminants from treated water. If you want a water filter for hiking or getting water from sources like creeks and rivers, you’ll need to be extra sure that the filtration system you’re buying can remove bacteria and other organisms found in nature.
While filters …

Many different types of filters are available to consumers. Determining which type is most appropriate for you—or whether you need a filter at all—depends on what functions you want a filter to provide. No filter eliminates all contaminants, so understanding what filters do and do not do is important.
Read the label to see if it is NSF-certified. If it is, you can search NSF’s databaseexternal icon to learn more about what a particular model is certified to protect you against. Labels on water filters also typically state the contaminants that are reduced, which can help to guide your choice. Be sure to read labels carefully yourself and verify the manufacturer’s claims with an independent source, as not all sales representatives will be familiar with your needs.
Keep in mind that most brands include many different types of filters. Sales people might be able to help you make an appropriate selection, but remember that they are sometimes paid to sell a particular brand. You should check claims and read the fine print on filter packaging for yourself and ensure that it will work for your purposes before purchasing.
Don’t assume that if the filter removes one contaminant, it also removes others. Filters that remove chemicals often do not effectively remove germs, and vice versa. Some water treatment devices that remove chemicals, such as reverse osmosis, ion exchange, or distillation systems, might also remove fluoride. Children who drink water with levels of fluoride <0.6 ppm might need a fluoride supplement. Check with your child’s pediatrician or dentist for specific recommendations.
The prices of different filtration systems can vary widely, from simple systems that can cost under $20 to complex systems costing hundreds of dollars and requiring professional installation. In addition to the price of purchasing and installing the system, consider the cost, schedule, and ease of maintenance, such as changing filter cartridges. In order to continue to work properly, all water treatment systems require maintenance.
Some filters are slow, while others can filter large amounts of water quickly. If you only need the filter for personal drinking water, you may not need a fast filter.
Filters commonly found in homes and stores include water filter pitchers, end-of-tap or faucet-mounted filters, faucet-integrated (built-in) filters, on-counter filters, under-sink filters, and whole-house treatment units. No filters or treatment systems are 100% effective in removing all contaminants from water, and you need to know what you want your filter to do before you go shopping (see Step 1). Not all filters of a particular type use the same technology, so you should read the label carefully.Water filter pitchers
Water filter pitchers are pitchers that are filled from the top and have built-in filters that water must pass through before being poured out for drinking or other use.
Refrigerator filters
Many refrigerators have a built-in filter that supplies water through the door and supplies an automatic icemaker.
Faucet-mounted filters
Faucet-mounted filtration systems attach to a standard faucet and can be switched on and off between filtered and unfiltered water flow.
Faucet-integrated (built-in) filters
Faucet-integrated filtration systems are faucets designed with built-in filters (instead of an attached filter, like a faucet-mounted system) and require installation.
On-counter filters
Faucet-integrated filtration systems are faucets designed with built-in filters (instead of an attached filter, like a faucet-mounted system) and require installation.
Under-sink filters
Under-sink filtration systems are installed under a sink and send water through a pipe to the filter’s own specially installed faucet.
Whole-house water treatment
Whole-house water treatment devices treat all water entering the house, not just the water used for drinking.
This table shows some benefits and limitations of a few popular home water treatment technologies. It does not include information on all filter types including many those that might remove germs via simple pore size filtration. Also see Technical Information on Home Water Treatment Technologies.
| Treatment Device | What it Does to Water | Treatment Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Activated Carbon Filter (includes mixed media that remove heavy metals) | Absorbs organic contaminants that acuse taste and odor problems.Some designs remove chlorination byproductsSome types remove cleaning solvents and pesticides | Is efficient in removing metals such as lead and copperDoes not remove nitrates, bacteria, or dissolved minerals |
| Ion Exchange Unit (with activated alumina) | Removes minerals, particularly calcium and magnesium that make water “hard”Some designs remove radium and bariumRemoves fluoride | If water has oxidized iron or iron bacteria, the ion-exchnage resin will become coated or clogged and lose its softening ability |
| Reverse Osmosis Unit (with carbon) | Removes nitrates, sodium, other dissolved inorganics and organic compoundsRemoves foul tastes, smells or colorsMay also reduce the level of some pesticides, dioxins, chloroform, and petrochemicals | Does not remove all inorganic and organic contaminants |
| Distillation Unit | Removes nitrates, bacteria, sodium, hardness, dissolved solids, most organic compounds, heavy metals, and radionucleidesKills bacteria | Does not remove some volatile organic contaminants, certain pesticides, and volatile solventsBacteria may recolonize on the cooling coils during inactive periods |
Source: EPA. Water on Tap: What You Need to Knowpdf icon…

If you think that your tap water can’t be improved then this article isn’t for you. In 2016, only 38% of participants said that ‘tap water is good quality in terms of taste and smell’ in the Consumer Council for Water’s Attitudes to Tap Water Report.
Despite the comparatively good standard of drinking water we have available it still has several impurities. In the case of tap water, odours, heavy metals and cleansing chemicals such as chlorine can remain present, causing unpleasant smells and tastes. In addition to these drawbacks, there can be adverse health affects associated regular consumption of water which inhabits these contaminants. We have also seen in various water crises that tap water is never 100% reliable.
You may think bottled water is the ideal solution, however, the cost of this both to your finances and the environment means that the best way to ensure your drinking water is of an adequate standard is to invest in a countertop water filter.
Here are 21 benefits you can access with filtered water:
Do you ever turn on the kitchen tap in a bid to rehydrate yourself only to baulk at the odour emanating from the water? Tap water is treated with a range of chemicals and is exposed to heavy metals which give it that unpalatable smell and taste that make it almost unbearable.
The potency of this odour can vary depending on the water quality in your area but one of the best benefits of filtered water is that you can make this odour thing of the past and give yourself clean drinking water.

Chlorine is the most common cleansing chemical used to treat water supplies in the UK. While chlorine is vital to remove dangerous bacteria and diseases from the water, the tiny proportion that remains can contribute to that tap water odour we’ve already discussed.
The US Council of Environmental Quality once found that cancer risk was 93% higher among those who were exposed to chlorinated drinking water.
The World Health Organisation also found an increased risk of bladder cancer among populations drinking chlorinated water versus those not exposed to chlorinated water over half of their lifetimes.

Drinking bottled water has become popular culture in the recent decade. The explosion of the fitness industry has coincided and aided the growth of people consuming a lot more bottled water. While this is positive from a public health perspective because people are increasingly opting for water over fizzy soft drinks, it is still needlessly expensive.
Bottled water can be up to 30x more expensive than water from a filter. Whether you’re buying it by the crate or religiously buying a bottle per day, you are massively overspending compared to the price per litre you receive from a water filter. This financial benefit of filtered water not only saves you money but gives you the same revitalising taste you expect from bottled water, straight from your tap.

The biggest problem with the surge in the bottled water market is that it’s ruining the environment. 1,000,000 plastic bottles are sold around the world every minute and less than half of the 480 billion plastic bottles sold in 2016 were properly recycled. It requires 17 million barrels of oil every year to produce the level of plastic bottles currently being consumed globally, and the amount of plastic produced each year is now the same weight as humanity!…

If you’re in one of the 15 million American households getting your water from a private well, the water your family uses for drinking, cooking, cleaning and bathing is your responsibility.
Without EPA oversight and regulations like public water supplies have, and with your well water quality dependent on the groundwater around you, it can be challenging to ensure a clean water supply. Especially when you consider:
So, why do we test water quality? In the case of well water quality, there could be many things that you can’t see, smell, or taste affecting your home and family. Your water will be affected by its environment which is constantly changing, so even if your water did not have a certain contaminant last year, it might have been introduced at any time.

There are many things you need to know about owning a well, including ways to improve the quality of your water supply. Here are the most common contaminants you need to know about.
Most groundwater will have trace amounts of these naturally occurring contaminants, but if there are large amounts of limestone, shale and coal nearby, you may have elevated levels impacting the groundwater feeding your well. If your water has a metallic taste and/or reddish/brown discoloration — which can also stain pipes and clothing — iron or manganese may be the culprit.
Does your water smell like rotten eggs? It could be hydrogen sulfide gas trapped inside your water coming from high sulfur content in the ground. If you live in a marshy area or on a farm near a manure pit, sulfides could be your issue. In addition to the bad odor, sulfides can corrode your plumbing and leave black stains anywhere you use a lot of water.
Copper, like iron, occurs naturally, but if your water has a blue/green discoloration, you may have corroding copper pipes, which might mean a bigger issue in your plumbing infrastructure or unusually acidic water flowing through those pipes. If your water has a significantly lower pH than 7, its acidic properties will strip the metal from your plumbing and faucets. Other sources of copper contamination in your groundwater could be mining or manufacturing activities close to you.

Having problems with hard water? High mineral counts from your bedrock are the likely cause, with calcium being the most common. Magnesium is another. As water passes through the ground, it dissolves any limestone or other rocks it comes in contact with carries these minerals with it into your home. While these contaminants rarely impact health, they can still cause a strange taste in the water, soap scum buildup, minor skin irritation and extra wear and tear on your water using appliances.
Better known as salt, extra sodium chloride can easily infiltrate your groundwater if you live along a highway or near a parking lot treated with road salt during winter months in colder areas of the country. The runoff could lead to a white residue in your water, alter the taste a bit and of course negatively impact you if you’re on a sodium-restricted diet. You also may see salt water intrusion if you own a home off the coast. Shifts in the weather can see the water from the ocean mix with groundwater more or less than usual.
The above items really only scratch the surface of chemicals and minerals that could invade your water supply. PFOS chemicals, arsenic and silica are other possible water contaminants to watch out for depending on your geographic area. Radon gas is another, which, for example, is colorless, tasteless, odorless and radioactive, which amplifies the need for testing.

Problems might not always be at the microscopic level. If dirt and sediment gets into your well pump, large particles and murky water could make it into your tap (along with any number of the above chemicals too). This could mean larger structural integrity concerns with your well, pump, tank or pipes.
If your faucets are sputtering before water flows normally, you have excess air in your system. While this won’t negatively impact your health, it’s still a contaminant in the sense that it’s something coming through that you don’t want to be there. More importantly, it could indicate a change in the water table, damage to your drop pipe or an issue with your well pump, so it’s an issue you should pay attention to.
Plant matter, leaf litter, insects getting inside your well cap and other environmental factors like erosion, flooding and fires can contribute to organic or inorganic particulate matter entering your water supply. Yellow or white/cloudy discoloration could be an indicator of such contamination, though it may not be quite so obvious.
In addition to organic and inorganic particles, there are chemical units that can combine with those compounds — like nitrates, or nitrogen-oxygen compounds. While they’re nutrients for plants, excess nitrates can leach into groundwater, especially following heavy rain or flooding. Fertilizers can also contain nitrates that could make it into your well water, especially considering they don’t bind well to soil. A variety of health issues are possible, especially for babies under 6 months old, but since nitrates are microscopic, it’s hard to tell they’re there without testing.
Bacteria like Giardia, or E. coli — can enter your water supply through animal waste like from a manure pit or sewage from a septic tank. Bacteria can also come from the bodies of decomposing animals that may have found a way into your well cap but were unable to find their way out. You can’t see or smell these bacteria, which makes testing that much more important, especially if you’ve had a sewage overflow or flooding recently. Storm or agricultural runoff could be all it takes for bacteria to make their way into your well water. While consuming water with bacteria in it isn’t harmful to your health, you might notice it giving you an upset stomach or diarrhea.

The National Groundwater Association (NGWA) provides online resources for homeowners with private wells at WellOwner.org. There you can learn more about well maintenance, water quality, and water treatment options.
While it’s important to know how a well works and keep up on basic maintenance yourself, the most important way to ensure safe water in the face of tasteless, odorless and colorless contaminants is through annual testing by a licensed professional. Samples of your water should be sent to a certified laboratory, which can give you detailed results about your water.
Ultimately, well water will never be perfect (neither will city water …
Clean up your drinking water with a pitcher, faucet attachment, or under-sink system.
You may not be able to control the quality of your well or municipal water, but you can use a filter to protect yourself and your family from potentially harmful contaminants—or just improve your water’s taste. We found the best options to make your water cleaner and healthier.
Check out quick info below of the top five water filters, then scroll deeper for buying tips and full reviews of these models plus other high-ranking options.
While the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates public water supplies, this doesn’t mean your water is totally free of certain contaminants like chlorine, asbestos, cadmium, copper, and fluoride. But in order to assess whether or not you should get a filter, you need to understand your water source and its potential contaminants.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends that if you get water from a private well, you get it tested at a state-certified lab at least annually. If you get water from a public system, you’ll get a report from the EPA on the quality of your drinking water that will come with your water bill and tell you what contaminants your water may have.
You may decide you want a water filter just to improve the taste of your tap water, even if you think the poor taste isn’t due to anything actually harmful to your health. However, the CDC warns that many contaminants cannot be seen, tasted, or smelled. If you confirm your water source may have harmful amounts of arsenic, nitrates, chlorine, lead, or other contaminants, you’ll want a water filter that can specifically address those concerns.
No filter will remove all contaminants, so it’s important to select the right type for your water source. We looked into all kinds of filters, from under-sink and countertop systems to faucet attachments, pitchers, and dispensers. The price range of water filters is vast, ranging from reverse osmosis models that cost hundreds to $20 pitchers. In addition to your water source and budget, you should consider the speed of the filter and your household size as well as how easy it is to install and maintain. You can search some filters in NSF’s database to learn in more detail about what contaminants each is designed to protect you from. The most common NSF/ANSI standards to be aware of include 42 (for removing chlorine and other bad tastes and odors), 53 (for reducing health contaminants like heavy metals), and 401 (for “emerging contaminants” like pharmaceuticals).

We researched ten expert sources and 27,000 consumer reviews to select the best water filters. To determine the Total Expert Score, we calculated the ratings from trusted publications, such as TechGearLab and Helpful Habitat, and converted them to a 100-point scale to make it easier for you to weigh the best options. Because more affordable faucet attachments, pitchers, and dispensers aren’t rated by enough sources for us to give them expert scores, we relied solely on consumer reviews for those models. Our Consumer Score represents the percentage of people who rated the product at least four out of five stars on retail and review sites like Amazon, Walmart, and Home Depot.
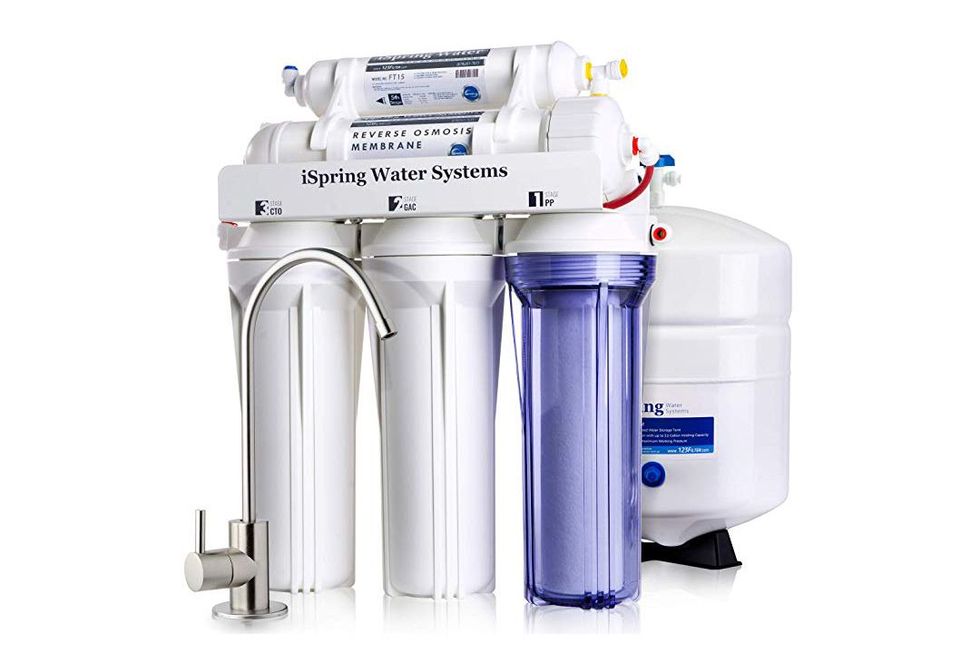

The iSpring RCC7 is a five-stage reverse osmosis filter that you can install under your sink to remove 99.9 percent of harmful contaminants (like lead and chlorine) that may be in your municipal or well water. TechGearLab awarded it Editors’ Choice for that, but also its ability to extract about 95 percent of salt. It comes with three pre-filters—a PP sediment, carbon KDF, and carbon block, which you should replace roughly every year. After water flows through those, a reverse-osmosis filter does the heavy-lifting of removing contaminants before a fine carbon GEC filter performs a final polish to deliver clean water to your faucet.
If you’re looking for something more permanent than a pitcher, this under-sink filter is easy to install yourself. Though the flow rate is on the low end for reverse-osmosis filters, it’s a rating of 75 gallons per day should provide plenty of clean drinking water even for a big family. Many Amazon reviewers also confirmed that the iSpring produced completely neutral-tasting water.

Total Expert Score: 84/100 | Consumer Score: 86% give it 4 stars or more
Rather than installing under the sink, this water filter sits on your countertop and attaches to most standard kitchen faucets. It’s an alkaline filter, meaning it adds healthy minerals like calcium, magnesium, and potassium back into your water while balancing the pH of the water to make it less acidic. It can also clean up to 750 gallons of water—or six to eight months’ worth for a family of four—before you need to replace the filter, though the replacement is relatively expensive. Amazon reviewers preferred Apex’s countertop filter for the health benefits associated with alkaline water, like immune system support and detoxification.

Total Expert Score: NA | Consumer Score: 65% give it 4 stars or more
Brita’s faucet-attachment filter reduces 60 contaminants, which is less than what a five-stage filtration system can do. But it still removes 99 percent of lead, chlorine, benzene, and other particles commonly found in tap water. On Amazon, one user said that Brita’s faucet filters “are effective for the well water that comes into my house, which has high sulfur content and very high iron content.”
This filter will last up to four months or 100 gallons—again, not as long as under-sink systems. However, the fact that the device is visible on your faucet instead of hidden away underneath your sink, along with the status indicator, helps remind you when it’s time to replace the filter.…
Content
You can also learn cyber security courses from institutes and companies. Diploma in Computer Science covers some major topics which include hardware, software, computer application & programming course covers topics like. Many reputed colleges and institutions are providing this computer science course. If you are a creative thinker and have a desire of learning computer classes then VFX and Animation is one of the best computer courses for you. Animations professionals and artist have an outstanding popularity and demand.
Python is used in many different areas. You can search for a job as a Python developer, data scientist, machine learning specialist, data engineer, and more. These jobs are interesting and in-demand. And, like other Python jobs, they pay good salaries.
So, I wanted to upskill myself in order to perform well in my current role. Fortunately, the EDW project in the company started migrating to Spark & Hadoop. The experience and the best courses knowledge I received in the Big Data Hadoop class helped me a lot to swiftly migrate to Hadoop. To get this before you graduate, plan on completing an internship in college.
Here are 22 popular IT skills that you can seize in 2022 to unlock your potential and advance your IT career. By building these skills, IT pros can add maximum value to any project they contribute to. Online courses are becoming a valuable resource to cut through the noise. If you have experience in these industries, there’s a growing demand for your help. There’s an ever-growing group of people that need help starting a new business.
There are 6.378 billion smartphone users in the world today, and that number is continuing to grow every year. This means that companies who want to stay relevant don’t just need websites; they need apps.
Programming languages touch nearly every IT job role, so IT pros would benefit from strengthening these skills. To some degree, everyone needs to learn the basics—at the very least. The great news is, that entrepreneurs and employees alike need access to these. There are niches within niches, and huge opportunities if you have the right skills to teach. There are no prerequisites for taking up online Data Analytics courses and anyone interested in pursuing a career in Big Data analytics can learn and grow in this field. A relatable example of using Big Data is in the production and development process of autonomous vehicles. The sensors present in these vehicles have the capability to drive on their own, capture vast amounts of data that can further be analyzed and used to improve their performance as well as, avoid accidents.
If you are not coming from engineering backgrounds, then also you can learn CCNA or CCNP, or both. Then you need to take some ad hoc classes for non-engineering students. The great number of fresher and experienced candidate, these days, are pursuing networking courses, if you are one of them, then CISCO technologies can be your choice. A majority of CISCO institutes want degree – graduation in any discipline.
When you start college, you’ll have to select what major you want to pursue and what degree is best for you. Accounting companies make up four of the top ten businesses in USA. Newly minted accountants in audit, tax, and corporate accounting are sought by both public and private accounting firms.
Helping you get started with an online teaching business is the reason I built OnlineCourseHost.com—to make this whole process much easier for you. Besides choosing the right topic to teach, there are many other pitfalls that you can fall into while creating an online course business. If you want to take advantage of profitable online course ideas, you need to bring them back to you. More than ever, people are conscious of their health and well-being. From personal fitness to mental health, they desire to optimize their lives. From affordable digital cameras to high-spec smartphones, we live in a visual world.
Assumes no prior Salesforce experience and provides real-world examples to illustrate the concepts you’re learning. #7 on LinkedIn’s emerging jobs report was Sales Development Representative, which mixes a traditional sales role with Salesforce technology expertise. As it’s not a purely technical role, it can be a good place to start within the broader universe of Salesforce.
Remember that eventually there will be online courses for literally everything, as any topic of human knowledge can be taught in a video, just like it can be taught in a classroom. You will also wonder about what online courses are in demand nowadays, according to the latest trends. If you are an online course creator like me, you are probably wondering if there is even any demand at all for your online courses, that you are planning on creating.…
Content
Please see /about to learn more about our global network of member firms. The goal of the “Three C’s” approach is to create a business environment in which FP&A interacts frequently and cohesively with the business.
“It is no longer enough to install basic financial systems and employ someone to maintain them,” Seidman said. “In a constantly changing world, companies must aspire to change with it.”
“With the advent of big data, more companies are able to utilize their information to perform analytics, identify drivers of performance, and make better business decisions in real time,” he said. That’s why financial planning and analysis (FP&A) consultant Carl Seidman recommends you transition to a more dynamic process by producing a rolling forecast. Weighing the Pros and Cons How efficient is your budget variance analysis process? See how your budget vs. actuals can drive organizational growth with our latest article. Businesses typically will use a defined period of time, such as on a monthly, quarterly, or annual basis to conduct their budget variance analysis.
Budgyt also imports and exports data from your existing general ledger accounting software. And that means that finance and business leaders are finalizing fourth-quarter forecasts and setting goals and plans for 2020. But with all this noise externally, how will organizations dial- in their final plans? And for each scenario, there’s more hard work to align financial goals with what are often fragmented sales, workforce, production and capital planning processes.
Instead, with monthly or quarterly reviews, department leaders are able to see variances and deduce possible explanations for differences from the original predictions. Then use those analyses as baseline to make adjustments in the plans for the upcoming quarters or months.
I created separate output section groups for the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement. I also created a “Supporting Schedules” section, where detailed processing calculations for PP&E and equity are broken down in order to make the model easier to follow and audit. In this article, we will only work on the assumptions and the income statement. Therefore, when forecasting over shorter periods , using revenues to predict SG&A may be inappropriate. Some models forecast gross and operating margins to leave SG&A as the balancing figure.
In this way, the forecast horizon continues to roll forward, based on the most current data available. The defined period can vary based on business preference and capabilities; common options include forecasting ahead by 12, 18 or 24 months or four, six or eight quarters.
Keeping communications consistent throughout of the entire process of introducing rolling forecasts is a top priority. For example, you present management with points such as greater risk awareness and the identification of new opportunities through more precise planning figures. Department heads are pleased about greater flexibility, for example, if the budget is adjusted during the year based on new findings, because current actuals suggest a higher level of engagement. Certain value drivers, such as prices or quantities, can be considered as well as non-financial data (e.g. effects of new competitors on the market, weather etc). In general, however, it is recommended to keep the various datasets for the forecast precise but manageable. This reduces the effort and expense involved, and at the same time optimizes your use of the tool.
Especially if you want to respond quickly to new opportunities and risks. Moving years’ worth of SharePoint data out of on-premises storage to the cloud can be daunting, so choosing the correct migration… The HR department of the largest U.S. county revamped its analytics stack in order to help reduce hiring times that often took … The vendor’s AI and machine learning capabilities have enabled the government agency to improve the effectiveness of its data …
Budgeting and forecasting software includes all the tools necessary for measuring and predicting financial performance. The most well-known financial forecasting methods compile important information about past, current, or upcoming financial decisions. An individual employee may have responsibility for specific segments of your financial data. If you need to receive input from multiple employees, using a manual approach to creating budgets can easily become impractical. You’ll likely be spending unnecessary time standardizing information into normalized formats. Furthermore, creating a budget is often a process that depends on working through multiple versions. Passing information back and forth multiple times can easily drain resources and generate costly delays.
In this step, FP&A analysts use the prepared data to create financial forecasts that predict how the business will perform in the future and if it is headed in the right direction. Financial forecasts include sales forecasts, cash flow projections, and more. Financial forecast models are also used to test out different scenarios, simulate the impact of different variables, and determine the best course of action to drive the right outcomes. Once all the necessary data is collected, it needs to be consolidated, standardized, and verified. Accurate plans, forecasts, budgets, and analysis all depend on the quality and completeness of the data they use – so this step is absolutely essential.
Finance organizations are being asked to do more with the same or fewer resources. This is driving the need to reduce or eliminate manual processes, and spend more time on analytics and supporting decision-making. The idea is that instead of managing the business based on a static budget that was created in the prior year, creating a rolling forecast is used to revisit and update budgeting assumptions throughout the year. This enables organizations to adapt plans and resource allocations based on changes in the economy, the industry, or the business. A rolling forecast is a report that uses historical data to predict future numbers and allow organizations to project future results for budgets, expenses, and other financial data based on their past results. How long it will take to transition from annual to rolling forecasts depends on the size of the company. But a gradated approach eases the burden and gives the best chance of success.
To accommodate this change, financial planning applications …